Student Loans
Old College Try
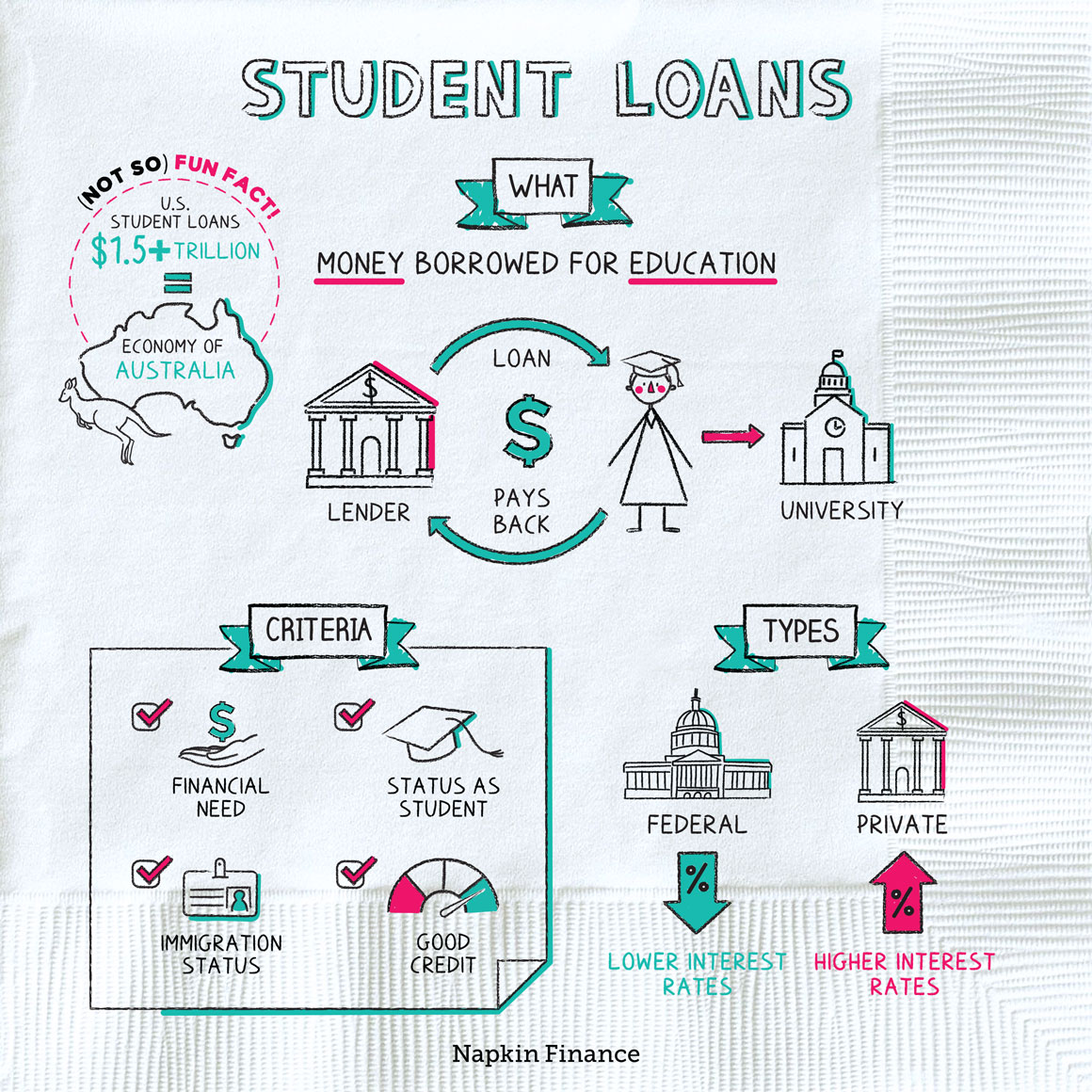
A student loan can be any kind of borrowed money that’s used to pay for education. Although the name might imply that the loans are only provided to students themselves, parents may also take out loans to help pay for their kids’ education.
There are two main types of student loans: federal loans and private loans. Federal loans are made by the federal government and come in a few varieties:
- Direct subsidized federal loans—low-interest-rate loans to students who demonstrate financial need.
- Interest doesn’t accrue on these loans while you’re still in school.
- Direct unsubsidized federal loans—low-interest-rate loans to students who don’t necessarily demonstrate financial need.
- Interest does accrue on these while you’re still in school.
- Parent PLUS loans—moderate-rate loans to parents, who have to pass a credit check in order to qualify.
- Parents have to start making payments on the loans while their child is still in school.
- Federal Perkins loans—low-interest loans to students with extreme financial need.
- This program expired in 2017 but could be reauthorized.
In contrast, private loans are generally made by private financial services companies, such as banks, credit unions, and Sallie Mae. Terms of private loans depend on the lender.
When deciding how to finance your education, there are some key distinctions you should know about federal and private loans.
| Federal loans | Private loans | |
| Who qualifies? | Anyone, but the type of loan generally depends on the family’s financial neediness | Those with a good enough credit score (or who have a cosigner with good credit) |
| When do you have to start making payments? | Usually not until after graduation (unless it’s a parent loan) | Often while you’re still in school |
| How high is the interest rate? | Usually lower | Usually higher |
| What if I can’t pay? | You may be able to take a temporary break from payments or opt into a new payment plan | Your lender may cut you a temporary break, but it’s not guaranteed |
| Could I get the loan forgiven? | Maybe, if you work in a public service career | Depends on your loan terms but less likely |
Not only are private loans typically more expensive than federal loans, they’re also usually less forgiving if you have trouble meeting payments later in life. Plus, many private loans charge a fee if you want to make additional payments or pay off your loan early. Federal loans don’t charge prepayment fees.
Depending on the lender or type of loan, you may need to show:
- Financial need
- Status as at least a part-time student
- Citizenship or immigration status
- A good credit history
When it comes to federal loans and some other types of aid, you’ll fill out the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) each school year to find out what types of loans you may qualify for.
Many families can’t fully cover the cost of college or grad school with savings, income, grants, and scholarships alone. Student loans help to fill that gap. The federal government sponsors a number of types of loans, while private lenders, such as banks and credit unions, also offer student loans. Federal loans are often considered a safer bet than private loans due to their typically lower interest rates and stronger protections when it comes to repaying.
- At more than $1.5 trillion, if Americans’ student loans were a country, they would be the thirteenth-largest economy in the world (roughly the size of Australia).
- More than half of student-loan borrowers wrongly assume their payments will be based on their income, and almost 10% wrongly believe they won’t have to pay off their loans if they can’t find a job.
- Student loans are funds borrowed to pay for education.
- The main types are federal loans and private loans. Federal loans are typically less expensive and come with extra protections for borrowers.
- Depending on the type of loan, you may need to demonstrate financial need, creditworthiness, your status as a student, and your immigration status in order to qualify for a loan.
- Filling out the FAFSA every year you’re in school can help you understand what types of loans you or your family may be able to qualify for.