IRR
Crunch the Numbers
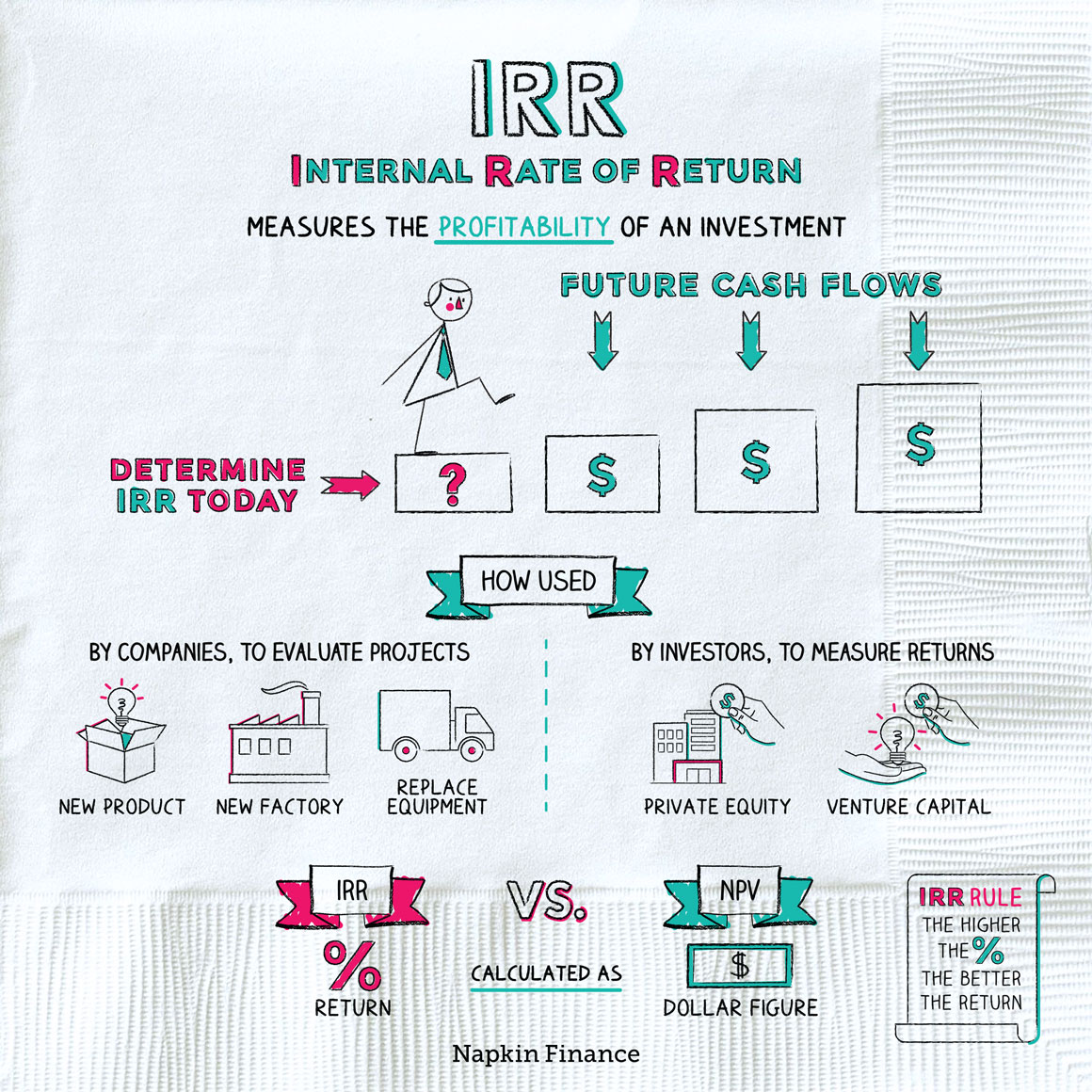
The internal rate of return, or IRR, is a measure of an investment’s or a project’s profitability.
Investors and companies use the metric to measure or estimate their returns on a particular use for their money.
The IRR can be used in two main ways:
| To estimate future returns | To measure past returns | |
| Data you need |
|
|
| What IRR tells you |
|
|
Companies can use IRRs to evaluate past or potential future projects, such as:
- Opening a store in a new market
- Buying new equipment
- Building a new factory
- Launching a new product
Investors can use IRRs to evaluate some types of investments. In particular, it’s often used with:
- Private equity
- Venture capital
The IRR isn’t the only metric companies have for evaluating projects. They can also consider a project’s net asset value, or NPV.
Here’s how IRRs and NPVs compare:
| IRR | NPV | |
| What it is | A percentage return figure | A dollar value |
| What it means | The annualized return rate the company earned (or expects to earn) on its project | The dollar amount of value the project adds to the company |
| Best uses | For evaluating a single project or multiple projects that aren’t mutually exclusive | For deciding which project to invest in if you have multiple options but you can only choose one |
The internal rate of return, or IRR, is one way a company or investor can calculate potential profitability of a project or an investment. It might help a business decide between different ways of spending money or help an investor measure returns on a venture capital or private equity investment. Generally, the higher the IRR, the better the investment.
- Choosing between investment options doesn’t have to be boring, especially if your choices are music royalties, collectible sneakers, or whiskey (these are all things people have actually parked their money in in hopes of a return).
- Studies have found that Tuesday is the most productive day of the week, so it’s probably best to save your IRR calculations for then.
- The internal rate of return, or IRR, can help you determine expected or past profits from a project or an investment.
- Calculating IRR depends on knowing how much cash you’ll put into the investment and when and how much cash you’ll receive back from the investment and when.
- Companies can use IRRs to help decide whether or not to replace equipment, launch a new project or service, or make an investment in a new factory.
- For individual investors, IRR is often used to calculate the performance of private equity and venture capital investments.
- Companies can also evaluate projects using their net present values, or NPVs, which instead distill a given project into a single dollar figure of value.