Blockchain
Chain Gang
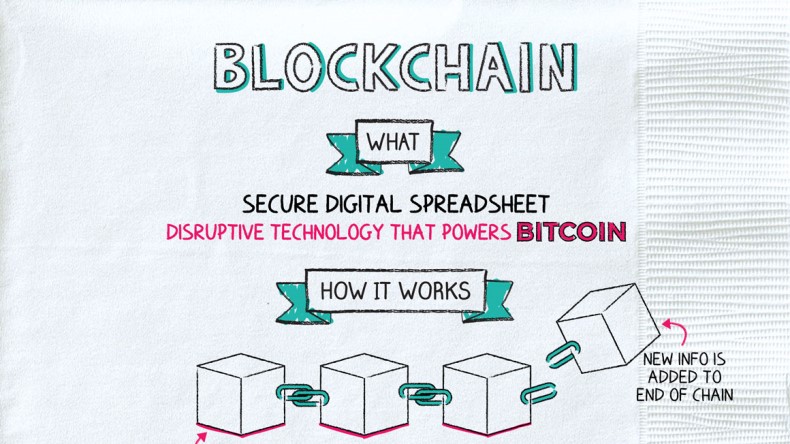

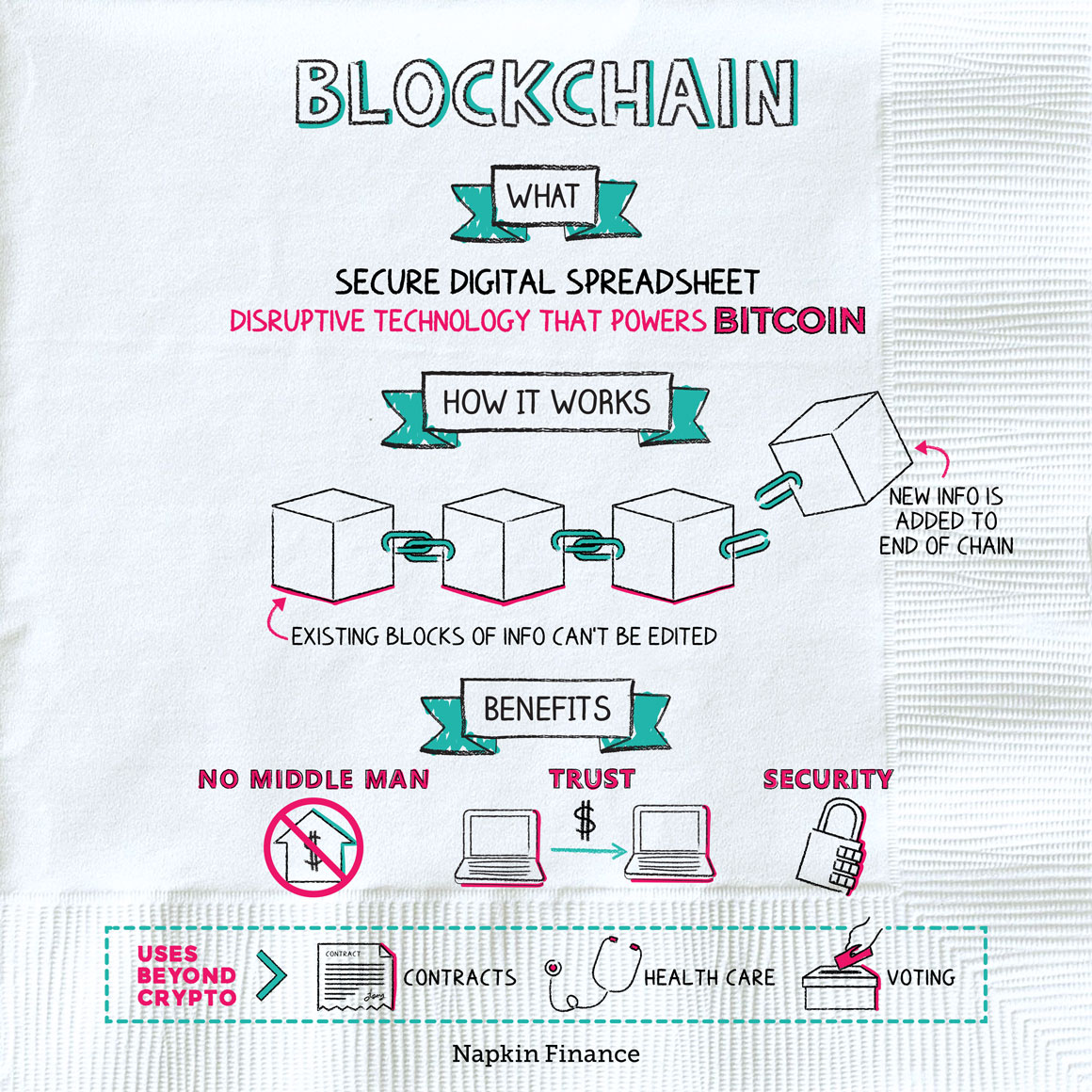
Blockchain is the recordkeeping technology that serves as the foundation for Bitcoin and some other types of cryptocurrencies.
The blockchain is like a huge public spreadsheet. But unlike something you create in Excel, once an entry is made in the blockchain, it is essentially unchangeable. That’s because the spreadsheet is encrypted and spread out over a wide network of users.
Instead of being able to edit existing entries, new entries are always added to the end of the chain (in “blocks”). And each block is connected to the one before it through a series of numbers. What you end up with is an unchangeable history of information.
To add a new block to the chain, a few steps have to happen:
Step 1: Transaction—To start the block, some type of transaction must occur. For example, someone sends money to another person.
Step 2: Verification—A network of computers confirms that the details of the transaction are correct. In the example of sending money, the computers verify the individuals involved, the amount, and when the transaction occurred.
Step 3: Storage—The verified transaction is stored in a block, which might contain hundreds of other transactions.
Step 4: Hash—That block is given an identifying code, or hash. The new hash is created from the previous block’s hash but is its own unique series of numbers and letters. The connection from one block to the next keeps the blocks from being changed or edited because changing one block would require changing hashes for every single block in the chain.
“Blockchains are record-keeping backed by fancy math.“
—Edward Snowden
The big advantages of Blockchain are:
- Trust. If a record can’t be edited (for example, the bank can’t accidentally erase a zero from the end of your account), then you can trust it.
- No middleman. Because the Blockchain is spread over a wide network, there’s no central person or group controlling the flow of information (or money).
- Security. Because the information is encrypted and decentralized, it’s essentially impossible for one person or organized group of people to hack it.
Bitcoin, arguably the world’s most successful cryptocurrency, depends on Blockchain both to keep track of the currency’s owners and for new Bitcoin to be created.
When someone completes a transaction, computers known as “miners” start attempting to solve complex math problems to verify the transaction.
Whichever miner solves the problem first (the answer acts as the miner’s “proof of work”) can add the next block. The miner earns Bitcoin as a reward. Each block is then tied to the one before it, forming a chain. These entries into the chain are time-stamped and become public and cannot then be modified or changed.
Blockchain is most often associated with cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, but it has the potential to disrupt countless other industries, including:
- Contracts—Whether transferring real estate or entering into a business contract, with Blockchain technology, all previously agreed-to terms could be public and verifiable but also secure.
- Healthcare—Medical providers could use the technology to share sensitive information in an efficient, secure way.
- Voting—Blockchain could serve as a secure, anonymous but verifiable technology for tallying votes.
Blockchain is a vast public record of transactions that cannot be edited or changed. This makes transactions more secure and difficult for hackers to tamper with. Bitcoin is the most well-known use of blockchain technology, but it could prove useful in other industries.
- Blockchain-powered Bitcoin uses more energy than 159 individual countries due to the energy intensiveness of mining for new coin.
- The musician Imogen Heap is using Blockchain to try to build a “fair trade” system for music so that artists can receive adequate pay for their work.
- Blockchain is the technology that powers Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
- The big innovation of Blockchain has been to create a system of recordkeeping that can’t be tampered with.
- Although it’s mainly used for cryptocurrency, Blockchain has the potential to be used in voting, contracts, the music industry, and more.